Kava vs L-theanine: Best for Stress Relief?
Dec 31st 2025
When stress hits, you need answers fast. Here’s the deal: kava and L-theanine are both natural options for calming your nerves, but they shine in different ways. Kava is great for unwinding after a long day, while L-theanine helps you stay calm and focused without slowing you down.
- Kava: Derived from a Pacific plant, it’s known for easing tension and promoting relaxation. Works well in the evening but comes with potential liver risks.
- L-theanine: Found in tea, it boosts “calm focus” by enhancing brain waves. Great for daytime use and pairs well with caffeine. Safer, with minimal side effects.
Quick Comparison
| Factor | Kava | L-theanine |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Relaxing after work | Staying calm and focused during the day |
| Onset Time | ~45 minutes | 30–40 minutes |
| Duration | Varies; typically a few hours | 8–12 hours |
| Side Effects | Possible liver issues, drowsiness | Minimal; rare mild effects |
| Safety | Avoid long-term use; liver precautions | Safe for most; avoid in pregnancy |
Bottom line: Use L-theanine to power through stressful workdays and kava to decompress at night. Want both? Combine them carefully for balanced stress relief. Always check with a doctor if you’ve got health concerns.
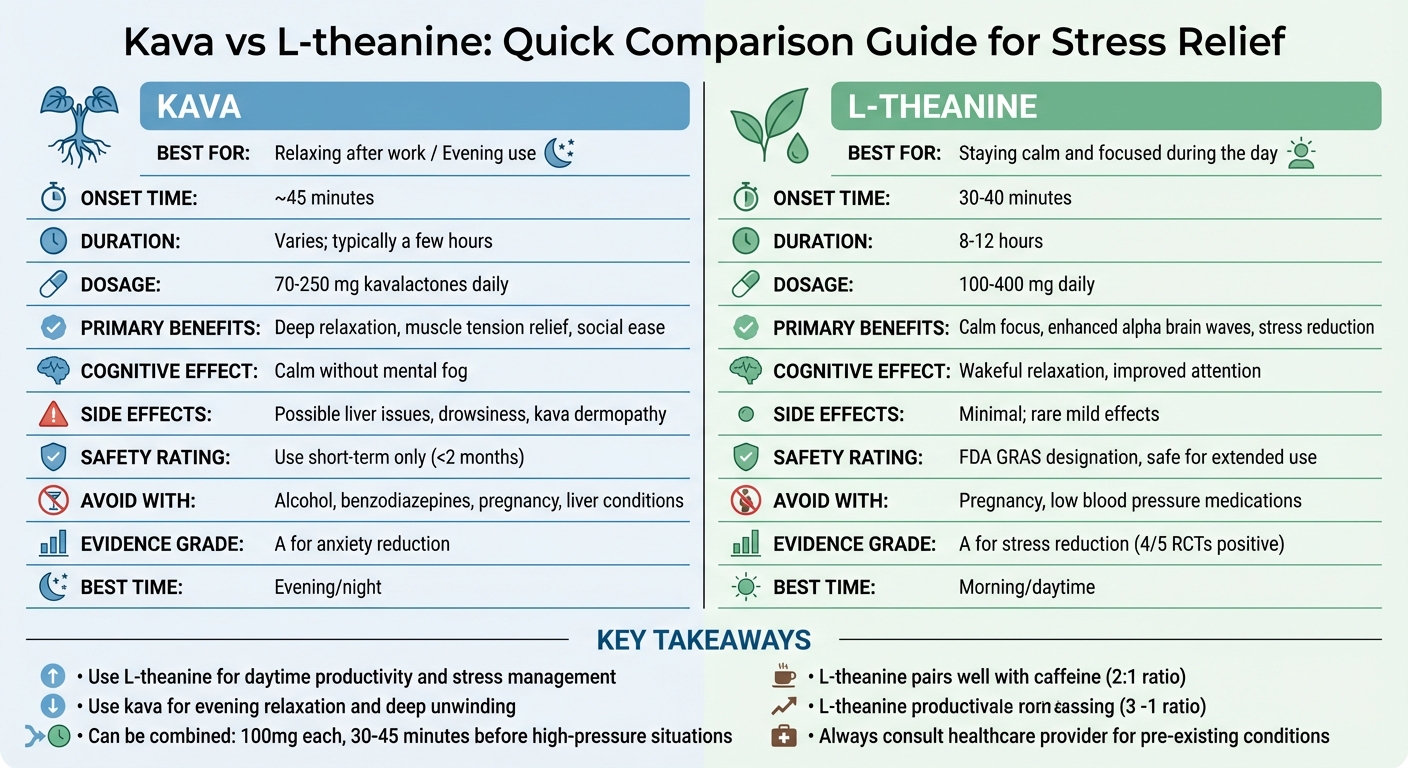
Kava vs L-theanine comparison chart for stress relief
What is Kava?
Kava (Piper methysticum) is a tropical shrub from the South Pacific, cherished for over 1,500 years in ceremonial and traditional beverages. Its active compounds, kavalactones (sometimes called kavapyrones), are concentrated in the plant's root. These kavalactones can cross the blood-brain barrier, helping ease stress and promote calm. Modern kava supplements often contain standardized extracts with about 70% kavalactones.
Traditional kava drinks typically start working within 5 to 15 minutes, while capsules or extracts may take closer to 45 minutes to kick in. A distinct feature of kava is the temporary numbing sensation it causes on the lips and tongue - an indicator of potent kavalactone content. Next, we’ll explore how kava achieves its calming effects.
How Kava Works
Kavalactones interact with several brain pathways to encourage relaxation without clouding the mind. They influence GABA receptors - the same system targeted by benzodiazepines - but without the mental dullness often linked to those medications. Additionally, kavalactones block norepinephrine reuptake and limit serotonin activity in the amygdala, the brain region tied to fear and anxiety. This combination fosters a state of calm alertness, where relaxation and focus coexist.
Dr. James Lake explains:
"When kava is used at recommended dosages (typically 60 to 300 mg/d), patients do not experience the mental slowing or impaired cognitive functioning that is typical of many conventional anti-anxiety medications."
Kava Benefits for Entrepreneurs
For professionals navigating high-stress environments, kava can be a practical ally. Certain types help ease anxious thoughts and encourage sociability during meetings, while others alleviate physical tension after long, demanding days.
Clinical studies show that daily doses of 250 mg kavalactones can significantly reduce anxiety, with up to 75% of participants reporting noticeable improvement.
Kava's safety profile is generally positive. Although liver toxicity has been a concern, the actual risk is estimated at less than 1 in a million doses. It has earned an "A" evidence grade for its effectiveness in reducing anxiety. To ensure safe use, avoid combining kava with alcohol or benzodiazepines, and opt for "Noble" kava varieties over "Tudei" types. These insights highlight how kava can support professionals during high-pressure workdays, which we’ll explore further in our comparisons.
sbb-itb-02d64da
What is L-theanine?
L-theanine (L-γ-glutamylethylamide) is a nonprotein amino acid primarily found in tea leaves from the Camellia sinensis plant. It’s what gives green tea its signature umami flavor and accounts for up to 50% of the amino acid content in these leaves. On average, L-theanine makes up 1% to 3.1% of the dry weight of tea leaves.
A typical 7-ounce cup of tea contains only 5.8–32 mg of L-theanine - far below the therapeutic range of 100–400 mg. This is why many people turn to supplements instead. Once consumed, L-theanine crosses the blood–brain barrier within 30 to 45 minutes, using the leucine transport system.
What sets L-theanine apart is its ability to create a state of "calm focus." It boosts alpha brain wave activity (linked to relaxed alertness) while dialing down beta waves (associated with nervousness and scattered thoughts). Unlike sedatives, it doesn’t cause drowsiness, making it an excellent choice for staying productive. Let’s dive into how it achieves this calming effect.
How L-theanine Works
L-theanine works by fine-tuning key neurotransmitters. It enhances GABA activity to quiet mental noise and increases dopamine and serotonin levels to stabilize mood. It also tempers the excitatory effects of glutamate by partially activating NMDA receptors. On top of that, it stimulates nitric oxide production, which can improve blood flow and help counter stress-related blood pressure spikes.
By increasing alpha brain waves (8–13 Hz), L-theanine promotes a state often described as "wakeful relaxation" or "calm attention." As researchers Roderick Dashwood and Francesco Visioli explain:
"The effects of L-theanine on alpha waves would appear to be divergent but can be explained by the induction of a state of 'calm attention.'"
L-theanine Benefits for Entrepreneurs
For entrepreneurs, L-theanine offers a powerful tool for maintaining focus and composure under pressure. In a randomized trial, participants taking 200 mg daily reported significant reductions in stress and agitation after just four weeks. It also improved sleep quality without causing daytime grogginess.
When paired with caffeine, typically in a 2:1 ratio, L-theanine amplifies focus and accuracy while softening caffeine’s jittery side effects.
Dr. Michael Murray, N.D., highlights its broad range of benefits:
"L-theanine reduces stress, improves the quality of sleep, diminishes the symptoms of the premenstrual syndrome, heightens mental acuity and reduces negative side effects of caffeine."
Beyond stress relief, L-theanine supports crucial skills like executive function and verbal fluency - essential for making decisions and communicating effectively in high-pressure situations. Its effects kick in within 30 to 120 minutes and can last 8 to 12 hours, making it a reliable ally for long workdays. For acute stress - like a big presentation or a critical meeting - taking L-theanine 30 to 60 minutes beforehand can help you stay sharp and composed.
Kava vs L-theanine: Effectiveness for Stress Relief
Scientific Evidence and Clinical Results
When it comes to stress relief, L-theanine shows consistent results, while kava's effects depend more on the context. A systematic review of five randomized controlled trials revealed that 4 out of 5 studies noted significant reductions in stress and anxiety with L-theanine doses ranging from 200–400 mg daily. Its calming effects usually kick in within 30–40 minutes and can last up to 8–12 hours.
Kava, on the other hand, presents a more complex picture. A study involving 60 adults with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) showed that a daily dose of 250 mg of kavalactones significantly reduced Hamilton Anxiety Scale scores within three weeks. Another multicenter study reported that 75% of participants found a standardized kava preparation (LI 150) as effective as medications like buspirone. However, a 16-week trial with 171 participants observed no significant difference between kava and a placebo for GAD remission rates (17.4% vs 23.8%).
Professor Jerome Sarris, an expert in Integrative Mental Health, sheds light on these mixed results:
"While research has generally supported Kava in non-clinical populations (potentially for more 'situational' anxiety as a short-term anxiolytic), this particular extract was not effective for diagnosed generalised anxiety disorder."
| Factor | L-theanine | Kava |
|---|---|---|
| Evidence Strength | Strong for acute stress (4/5 RCTs positive) | Strong for situational anxiety; mixed for clinical GAD |
| Anxiety Reduction | Significant improvements at 200–400 mg | 250 mg kavalactones reduced HAS scores in 3 weeks |
| Onset Time | 30–40 minutes | ~45 minutes |
| Duration | 8–12 hours | Varies by dose and variety |
| Cognitive Impact | Enhanced attention and reaction time | Potential for mild memory impairment in some users |
These findings highlight how each supplement fits into different stress management scenarios.
Practical Use Cases for Entrepreneurs
For entrepreneurs juggling high-pressure environments, L-theanine and kava can serve complementary roles. L-theanine is ideal for maintaining focus during busy work hours. A dose of 100–200 mg in the morning can help you power through meetings, presentations, or deep work without causing drowsiness.
Kava, on the other hand, shines in the evening. After a demanding day filled with decisions and problem-solving, kava can help you unwind. Its physical muscle relaxation and mental calming effects make it a great alternative to alcohol for decompressing. Think of it as a way to ease tension - like a massage in a cup.
For acute stress situations, such as pitching to investors, L-theanine taken 30–40 minutes beforehand can help you stay calm and collected. If you're dealing with chronic stress that disrupts sleep or recovery, kava in the evening can help quiet your mind and prepare you for rest. By tailoring your supplement choice to your daily stress patterns, you can strike a balance between peak performance and recovery.
Side Effects and Safety Profiles
When considering kava and L-theanine, it's important to weigh their safety profiles alongside their potential benefits. Here's a closer look at the risks and precautions tied to each.
Kava Safety: Risks and Precautions
Kava is generally safe for short-term use, typically under two months, but extended use can pose serious health risks. Over 100 cases of liver toxicity, some requiring liver transplants, have been associated with kava consumption, as reported by Examine.com.
Prolonged use may result in kava dermopathy, a condition causing dry, scaly skin and temporary yellow discoloration. Other common side effects include headaches, dizziness, and gastrointestinal discomfort. Kava's sedative effects can be severe enough to impair activities like driving or operating machinery, with some users even receiving driving-under-the-influence citations.
Combining kava with alcohol or benzodiazepines is especially dangerous, as it can amplify liver stress and sedation. The World Health Organization advises limiting intake to no more than 250 mg of kavalactones daily. Additionally, kava should be discontinued at least two weeks before surgery due to potential interactions with anesthesia.
Certain groups should avoid kava entirely:
- Pregnant individuals, as it has been linked to a 2.5 times greater risk of low birth weight.
- Those with pre-existing liver or Parkinson's disease.
L-theanine Safety: Risks and Precautions
L-theanine stands out with a very mild side-effect profile. It is well-tolerated at typical doses of 100–400 mg per day for up to two months, with clinical studies showing no significant adverse effects even at doses as high as 900 mg daily.
"L-theanine exhibits a good safety profile based on toxicology studies... doses of l-theanine used to promote relaxation did not have hypnotic or sedative side effects."
Unlike kava, L-theanine fosters a state of "calm alertness" without causing drowsiness or impairing cognitive function. There are no documented cases of liver toxicity, dependency, or severe drug interactions.
However, there are a few precautions:
- Those taking medication for low blood pressure should monitor for potential additive effects, as animal studies suggest L-theanine may lower blood pressure.
- It should be avoided during pregnancy and lactation, as it crosses the placenta and enters breast milk.
- Long-term safety beyond three months of use remains unclear.
Comparison Table: Side Effects and Precautions
| Factor | Kava | L-theanine |
|---|---|---|
| Common Side Effects | Headache, dizziness, GI upset, drowsiness | Minimal; rare mild tics |
| Serious Risks | Liver toxicity (100+ cases); kava dermopathy | None documented for standard use |
| Sedation Level | High; impairs motor function and concentration | Low; promotes calm alertness |
| Alcohol Interaction | Dangerous; increases sedation and liver stress | No significant interaction reported |
| Dependency Risk | Rare psychological dependency possible | No known risk of dependency |
| Pregnancy Safety | Avoid; 2.5× higher risk of low birth weight | Avoid; crosses placenta and breast milk |
| Long-term Use | Skin changes, potential liver damage | Insufficient data beyond 3 months |
Understanding these safety profiles is key to making informed decisions about incorporating kava or L-theanine into your routine. Each comes with its own set of considerations, especially for long-term use or specific health conditions.
Dosage, Usage, and Suitability for High-Pressure Lifestyles
Balancing stress relief with productivity is crucial, especially for those with demanding schedules. Finding the right dosage ensures these supplements support your goals without slowing you down. Kava and L-theanine each have unique ways of fitting into busy lifestyles.
Kava Dosage and Usage Tips
Clinical studies suggest kava extract doses ranging from 100–400 mg, delivering 60–300 mg of kavalactones. For most, 70–250 mg is effective for managing stress while maintaining mental clarity .
For daytime use, opt for lighter kava strains that promote relaxation and improve mood without causing drowsiness. Save higher doses for the evening to aid recovery and relaxation.
"Kava is known to produce a calming state without causing an individual to lose any degree of focus or mental clarity." - Steve Shaw, Tiger Fitness
Choose products standardized for kavalactone content to ensure consistency. To protect liver health, limit kava use to short-term periods (less than two months) and avoid mixing it with alcohol or sedatives.
L-theanine Dosage and Usage Tips
L-theanine is perfect for maintaining calm focus during work. Effective doses range from 100–400 mg, with 100–200 mg being the sweet spot for most people. Its effects kick in within 30 minutes and can last up to 12 hours .
For an energy boost without the jitters, pair 100 mg of L-theanine with your morning coffee. Even smaller doses, like 50 mg, can sharpen mental alertness and improve focus.
"L-theanine might be the closest thing we've got so far to meditation in a capsule." - Klara Mudge, Functional Medicine Nutritionist
On hectic days, taking 100–200 mg up to three times can help manage stress effectively. Stick to safe limits - no more than 600 mg within six hours or 1,200 mg in a single day. Unlike kava, L-theanine’s non-sedative nature keeps you sharp and productive throughout the day.
Kava and L-theanine in Combination
Pairing kava with L-theanine offers a balanced approach to easing both physical tension and mental stress. Kava interacts with GABA, serotonin, and dopamine pathways to ease muscle tension and promote social relaxation. Meanwhile, L-theanine boosts alpha brain wave activity, encouraging a calm yet focused state of mind. Together, they provide relaxation without the mental fog or drowsiness that might hinder productivity.
L-theanine typically begins working within 30 minutes and lasts up to 12 hours, while kava takes about 45 minutes to kick in. For best results, take both supplements 30–45 minutes before high-pressure situations. This timing creates a state of "attentive calmness", blending relaxation with sharp focus - ideal for maintaining performance during stressful moments.
To get started, try 100 mg of each and adjust based on your tolerance. Some ready-made formulations combine these ingredients into easy-to-use relaxation drinks. For those seeking better sleep, kava may support REM sleep quality, while L-theanine can improve overall sleep efficiency.
Safety Reminder: Avoid combining kava and L-theanine with alcohol or other sedatives. Limit kava use to short-term periods (no more than 8 weeks) to minimize potential liver enzyme risks. If you're on medication or have any liver concerns, consult a healthcare professional before using these supplements.
Conclusion: Which is Best for Stress Relief?
When it comes to stress relief, the right choice depends on your schedule and specific needs. For daytime stress management, L-theanine shines as a go-to option. It promotes calm focus without making you drowsy, making it perfect for staying productive under pressure. Backed by an FDA "Generally Recognized As Safe" (GRAS) designation and an Examine Evidence Grade A for reducing stress symptoms, it’s a reliable pick. Taking 100–200 mg alongside your morning coffee can help smooth out caffeine jitters, keeping you sharp during intense meetings or focused work sessions.
Kava, on the other hand, is better suited for unwinding in the evening. Known for easing anxiety and relieving muscle tension, it’s great for deep relaxation after a long day. However, kava comes with a caution: it poses risks to liver health. Use it sparingly and avoid it altogether if you have liver concerns.
"L-theanine delivers calm focus without drowsiness, making it the perfect natural supplement for our high-stress, high-performance world." – Dr. Andrew Kerklaan, DC
For busy professionals juggling demanding schedules, L-theanine offers a safer, more flexible solution for everyday stress. Its ability to keep you calm yet alert makes it an excellent choice for maintaining steady performance. Meanwhile, reserve kava for those rare moments when you need to fully decompress. By aligning your supplement use with your daily rhythm, you can tackle stress effectively while staying at the top of your game.
FAQs
What’s the difference between kava and L-theanine for stress relief?
Kava and L-theanine both address stress, but they take entirely different approaches. Kava relies on compounds called kavalactones, which act as gentle sedatives and muscle relaxants. This can lead to a deeply relaxed, even slightly drowsy state. However, the effects often require consistent use over several weeks to become noticeable. It's worth noting that kava carries a rare risk of liver-related side effects, so caution is advised.
In contrast, L-theanine promotes a calm, focused state without sedation. By boosting alpha brain waves, it helps ease anxiety while keeping you alert. Many users describe feeling relaxed yet clear-headed, with minimal or no side effects. This makes L-theanine a solid choice for staying productive while managing stress.
Is long-term use of kava safe?
Long-term consumption of kava has been linked to uncommon but serious risks, such as potential liver damage. Additionally, some individuals have reported side effects over time, including apathy, weight loss, and other general health concerns.
If you're thinking about using kava to help with stress, it's crucial to approach it responsibly. Speak with a healthcare professional, particularly if you have existing health conditions or intend to make it a regular part of your routine.
Is it safe to combine kava and L-theanine for managing stress?
Yes, you can combine kava and L-theanine for stress relief, but it’s crucial to proceed carefully. Kava has been linked to rare cases of liver issues, so sticking to the lowest effective dose is key. Always consult a healthcare provider before using these supplements together.
If you decide to include both in your routine, pay close attention to how your body reacts and prioritize your well-being. It’s especially important to talk to your doctor if you have existing health conditions or are on other medications.


